IFSC and MICR Code
Find IFSC and MICR Codes of all banks in India
Or Choose Bank from list below
IFSC Code & MICR Code: Meaning, Uses, and How They Work
In today’s digital banking world, two codes are very important for smooth money transactions in India — IFSC code and MICR code.
- The IFSC code is used for online money transfers like NEFT, RTGS, and IMPS.
- The MICR code is used for cheque processing and clearance
Both these codes are unique identifiers that help banks and the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) make payments faster, safer, and more accurate. Let’s understand them in detail.
What is IFSC Code?
The Indian Financial System Code (IFSC) is an 11-character alphanumeric code given to every bank branch that provides online fund transfer services.
- First 4 characters → represent the bank name.
- 5th character → always 0 (reserved for future use).
- Last 6 characters → represent the branch code.
→ Example: HDFC0001015
- HDFC = Bank name
- 0 = Reserved digit
- 001015 = Branch code (Dalhousie, Kolkata)
The IFSC code is issued by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and is mandatory for all branches participating in NEFT, RTGS, and IMPS transactions.
Why is IFSC Code Important?
The IFSC code is mainly used to make electronic fund transfers in India. Here are its major uses:
- Online Money Transfers - Required for NEFT, RTGS, and IMPS transactions.
- Adding Beneficiaries - Needed while adding a new recipient in net banking or mobile banking.
- Cheque Clearing - Helps in faster ECS (Electronic Clearing System) settlements.
- Loan EMI Payments - Used for auto-debit and EMI deductions.
- Utility Bill Payments - Required when paying bills through online banking.
How Does IFSC Code Work?
When you transfer money online:
- The sender enters the recipient’s bank name, branch, account number, and IFSC code.
- The sending bank uses the IFSC to identify the correct bank branch.
- RBI routes the money through NEFT/RTGS/IMPS to the beneficiary’s bank.
- The receiving bank verifies the IFSC and deposits money into the right account.
This system makes transactions fast, accurate, and secure.
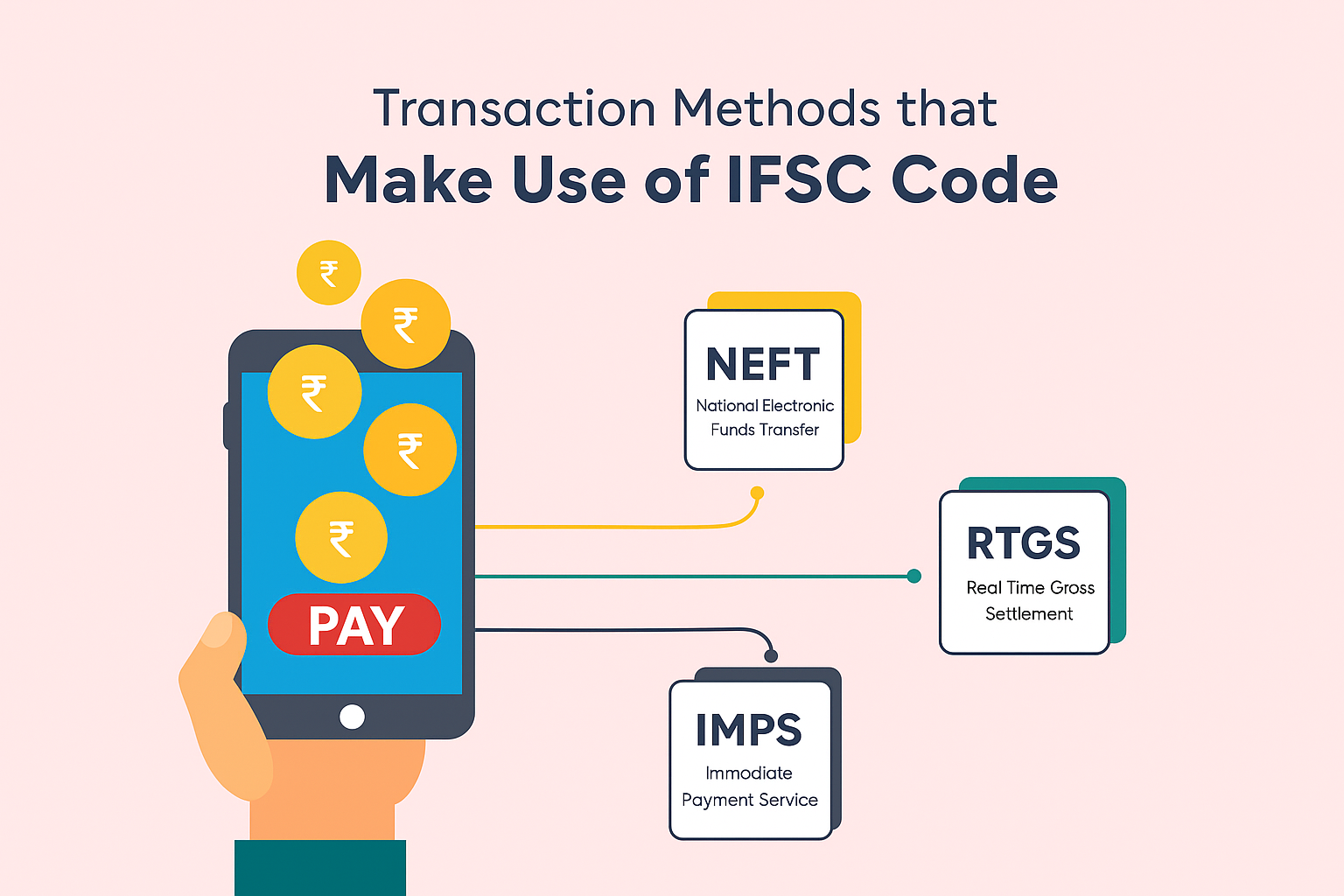
Modes of Transfer Using IFSC Code
- NEFT (National Electronic Fund Transfer) – Funds are settled in hourly batches. Safe and RBI-monitored.
- RTGS (Real Time Gross Settlement) – Instant, large-value transactions (usually above ₹2 lakh).
- IMPS (Immediate Payment Service) – 24x7 instant transfers via net banking, mobile banking, or SMS.
This system makes transactions fast, accurate, and secure.
How to Find IFSC Code?
- Cheque Book – Printed at the top along with branch address.
- RTGS (Real Time Gross Settlement) – Instant, large-value transactions (usually above ₹2 lakh).
- IMPS (Immediate Payment Service) – 24x7 instant transfers via net banking, mobile banking, or SMS.
What is MICR Code?
→ Example: 700002021 (SBI, Kolkata Main Branch)
- First 3 digits → City code
- Next 3 digits → Bank code
- Last 3 digits → Branch code
Unlike IFSC (used for online payments), MICR is used for cheque-based transactions.
Why is MICR Code Important?
MICR code is used to:
- Speed up cheque processing – Machines quickly read details with magnetic ink.
- Prevent fraud – Difficult to duplicate or tamper.
- Ensure accuracy – Helps in error-free clearing of large cheque volumes.
- Support global transfers – Used in some international fund transfers.
IFSC Code vs MICR Code (Key Differences)
| Feature | IFSC Code | MICR Code |
|---|---|---|
| Full Form | Indian Financial System Code | Magnetic Ink Character Recognition |
| Purpose | Online fund transfers (NEFT, RTGS, IMPS) | Cheque clearance |
| Format | 11 characters (alphanumeric) | 9 digits (numeric) |
| Where Found | Printed on cheque (top) & passbook | Printed at bottom of cheque leaf |
| Example | SBIN0001707 | 110229003 |
Where to Find Them on a Cheque?
- IFSC Code - Printed on the top (along with branch details).
- MICR Code - Printed at the bottom (next to the cheque number).

Example: IFSC & MICR of Popular Banks
| Bank Name | IFSC Code | MICR Code | Branch |
|---|---|---|---|
| SBI | SBIN0000691 | 110002087 | New Delhi, Sansad Marg |
| ICICI Bank | ICIC0000002 | 560229002 | Bangalore, MG Road |
| Axis Bank | UTIB0000373 | 400211033 | Mumbai, Goregaon East |
| HDFC Bank | HDFC0002649 | 110240312 | Noida, Gautam Buddha Nagar |
FAQ's
1. Who issues IFSC codes?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
2. Can two branches have the same IFSC?
No, each branch has a unique IFSC.
3. What if I enter the wrong IFSC during transfer?
Your transaction will fail or get rejected.
4. Is MICR code mandatory for online transfers?
No, it is only used for cheque processing.
5. Are IFSC and SWIFT codes the same?
No. IFSC is for Indian transfers; SWIFT is for international transfers.